fungi life cycle explained
There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi. Order Toll Free US Canada.
The Life Cycle of Fungi.

. Their role is to produce and release spores the fungal equivalent to. Meiosis reduction division restores the haploid. In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of ascomycetes explained with the help of a suitable diagram.
Fungi life cycle explained Sunday March 13 2022 Edit. The life cycle of a mushroom begins and ends through five stages of evolutionary phases beginning as a fungal spore seeds and completing its cycle as a mature fruiting. Fungi are subdivided on the basis of their life cycles the presence or structure of their fruiting body and the arrangement of and type of spores reproductive or distributional.
There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way. 2022 Fungi Perfecti LLC PO Box 7634 Olympia WA 98507 USA.
Life cycle of fungi. Asexual reproduction takes place by uninucleate thin-walled spores which are referred to as. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts moulds and mushrooms.
The life cycle inventory phase involves the compilation of elementary flow data ie flows that pass. The organism is haploid and has no diploid phase except for the sexual. The fused hyphae containing haploid nuclei from two.
The mycelium in most species of Taphrina is annual but in some species it is perennial. Fungal life cycles spores and more. Div1 Div1 Fungi Microbiology Fungus Reproduction Youtube Characteristics Of Fungi Boundless Biology Life.
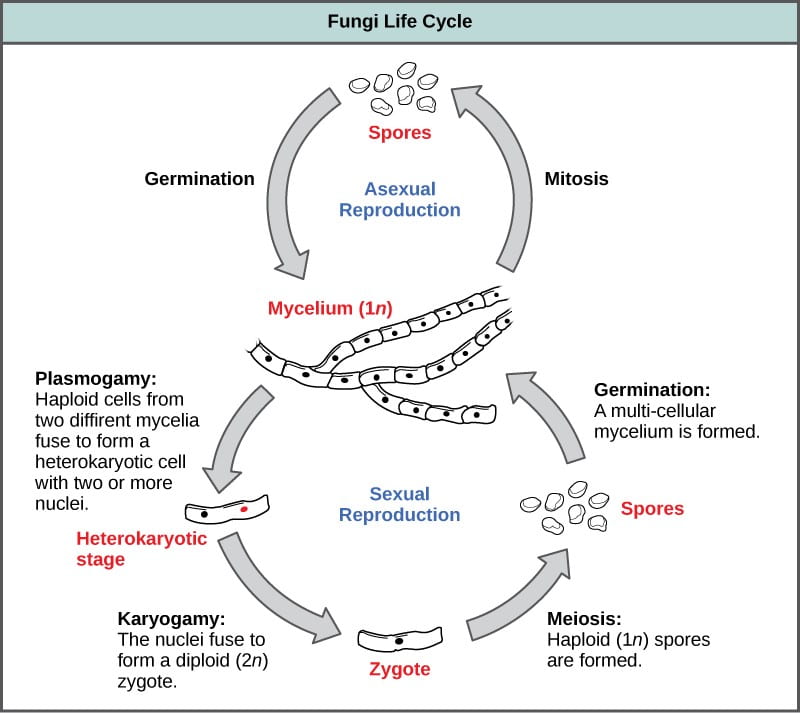
Life Cycle of Ascomycetes With Diagram Fungi. The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi.
Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase. While some fungi reproduce sexually others.
In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. The fungus spends most of its life cycle in this state and only forms mushrooms under specific conditions. In these cells genetic material from the parent fungi combines and divides to form spores.
In reality there are many sub-steps of the process. Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation. Despite their diversity in.
Some fungi are multicellular while others such as yeasts are. These spores also contain enough nutrients to support germination when it occurs.

24 1c Fungi Reproduction Biology Libretexts

A Detailed Explanation Of The Mushroom Life Cycle Grocycle

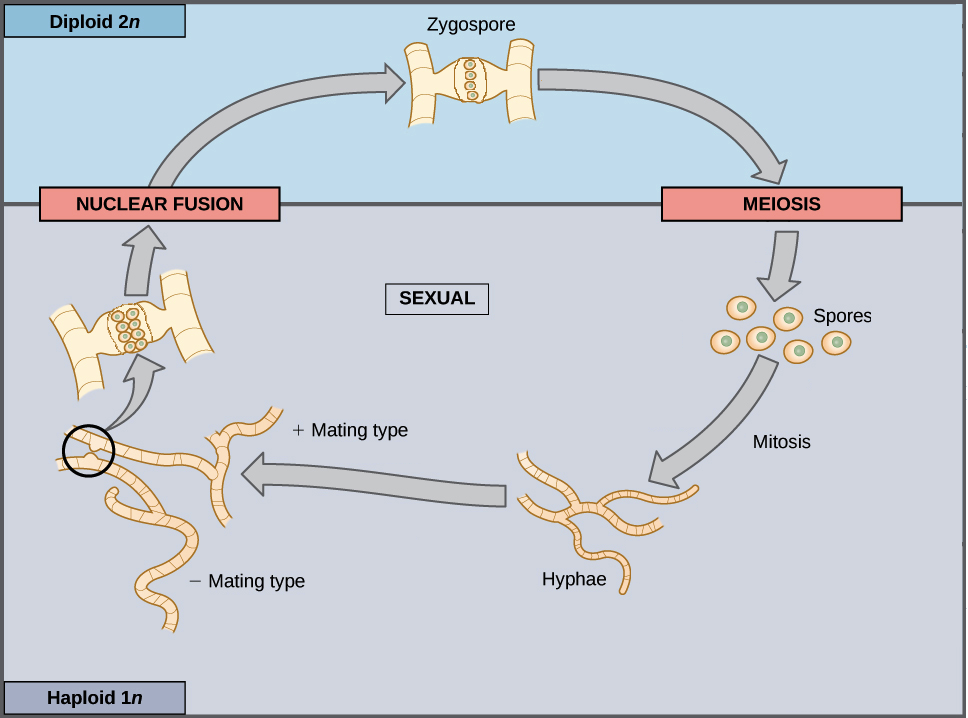
Zygomycota The Conjugated Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Life Cycle Of An Am Fungus And The Different Steps During Am Development Download Scientific Diagram

Diagrammatic Representation Of Mushroom Life Cycle Download Scientific Diagram

Diagrammatic Representation Of Mushroom Life Cycle Download Scientific Diagram

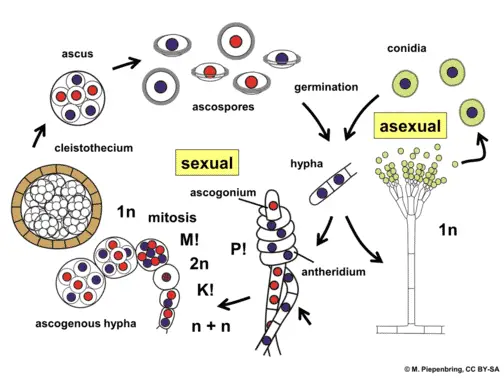
Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology For Majors Ii
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity
Sexual Life Cycles Article Meiosis Khan Academy
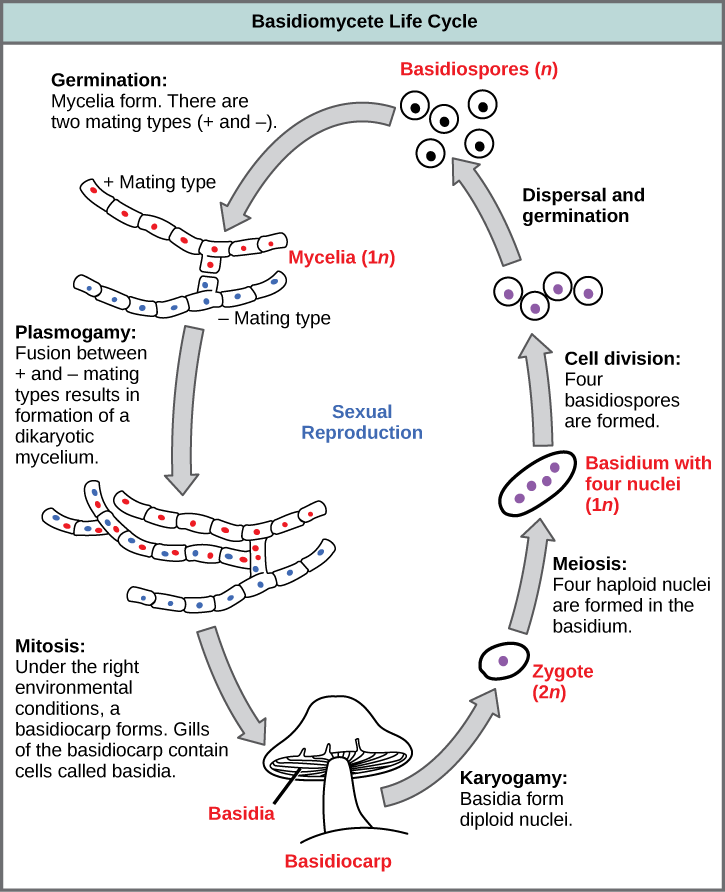
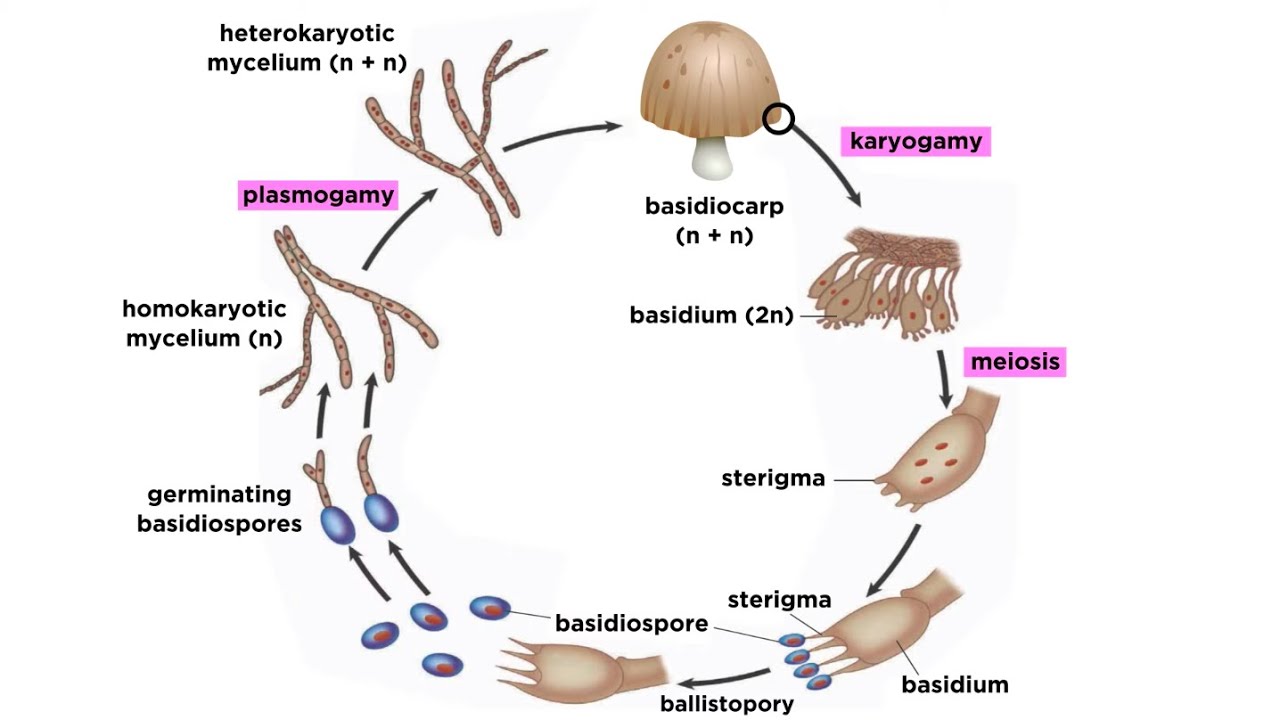
Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids
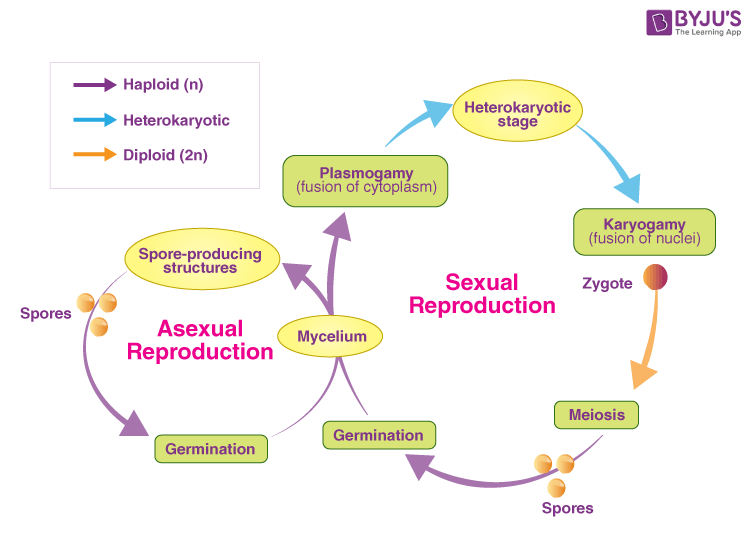
Fungi Life Cycle Introduction Life Cycle Faqs

Characteristics Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e